Thimal Caldera
2025-01-17
Content
- Introduction
- Understanding the Modern Stock Market Dynamics
- Evolution of Stock Market Prediction
- Predicting Stock Prices with LSTM and Sentiment Analysis
- Real-World Applications in Financial Markets
- Conclusion

1. Introduction
What if the stock market feels less unpredictable? Often known as a fast-moving, high-stakes environment in which fortunes can change in an instant, the volatility of the stock market is a source of both excitement and concern. While this perspective is true to some extent, understanding their underlying mechanics reveals a more systematic reality; beneath the surface volatility lies a vast network of data points, market signals, and interconnected factors that influence price movements.
The stock market functions as a critical platform for companies to raise essential growth capital. Simultaneously, it offers investors opportunities to build wealth. However, the way across the market is fraught with risks. Prices could be driven by a complex interplay of influences ranging from economic circumstances or geopolitical events to changes in investor sentiment. In recent years, traditional methods of analyzing the stock market, such as statistical models and fundamental analysis, have struggled to keep up with the increasing complexity of today’s global financial systems. Events like the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how market sentiment shifted rapidly in response to real-time data like infection rates, lockdown policies, and vaccine progress. These dynamic factors were often too slow or narrow in scope for conventional models, which could not adequately capture these fast-moving changes. The result? Delayed insights and missed opportunities for investors to respond strategically in volatile conditions. Therefore, there is a need for a new paradigm with a data-driven approach in market analysis.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a promising solution to this new paradigm. Its ability to process large and variegated data, far exceeding what human analysts or traditional models can handle, has enabled it to uncover patterns and anomalies that might not be apparent for conventional tools. From identifying subtle outliers in trading data to analyzing real-time news and social media to gauge market sentiment, AI is shifting how investors approach decision-making. The efficiency at which the data is inferred allows investors to navigate the complexities of the stock market, offering valuable insights that support more timely and informed responses. As we explore how AI is reshaping the future of financial forecasting, it’s clear that we’ve only begun to scratch the surface. Let’s dive deeper into how AI is transforming the way we understand the market today and what it holds for the future of investing.
2. Understanding the Modern Stock Market Dynamics
The stock market is a very large and active trading arena for ordinary shares of public limited companies. Shares, often referred to as stocks, represent partial ownership in a company, granting shareholders a proportional claim on its assets and earnings through their investment. The stock market serves as a critical conduit for capital flow, enabling companies to raise capital for expansion, innovation, and operational improvements while providing investors with opportunities to allocate capital toward ventures aligned with their risk appetite and growth expectations. The stock market’s liquidity makes it easy for investors to buy or sell shares, enabling effective portfolio management. Investing in several companies can diversify risks, and the return potential can increase.
The stock market is popular for its volatility, where prices can rise or fall quickly, making it an exciting but unpredictable place. Economic conditions, political events, and social trends drive this. For instance, when Tesla unveiled its Cybercab robotaxi on October 10, 2024, the event garnered substantial public attention. However, the presentation lacked detailed technical information and clear timelines, leading to investor skepticism. Consequently, Tesla's stock dropped approximately 8.8% the following day as investors reassessed the company's future prospects in the autonomous vehicle market. This illustrates how the market's reaction to product announcements can be heavily influenced by the depth of information provided and the perceived feasibility of the company's plans. Similarly, political events can cause significant instability in the stock market. For example, during the 2024 U.S. presidential election, uncertainty surrounding the policies of potential candidates and their impact on key industries like energy and healthcare contributed to market fluctuations. As investors speculated on proposed reforms, there was a surge in buying and selling sector-specific stocks, highlighting how sensitive markets can be to political dynamics and the decision-making process. Likewise, changes in interest rates, such as hikes that make loans less accessible, can reduce corporate profits and lead to declining stock prices. Conversely, business tax reductions can enhance investment ability, boosting share values. While these events are inherently unpredictable, they rarely go unnoticed. They often appear in newspapers or social media platforms. Public reaction to such news drives market fluctuations as people interpret and respond to the information.
Imagine a scenario where two major publicly traded companies announce a sudden merger. Following their official media release, the news quickly goes viral, appearing as a main topic in newspapers, trending across social media platforms, and sparking widespread public discussions. Millions of people begin commenting and sharing their opinions about the merger, making it one of the most talked-about topics in financial and business circles.
Analyzing this massive influx of sentiment-rich data becomes essential if a stock analyst wants to predict how this merger will impact the stock prices of the companies involved and the broader indices. However, manually processing all the relevant news articles, social media posts, and public opinions is practically impossible due to the sheer volume of data generated in real time. This is where AI excels. Deep learning models in AI can efficiently evaluate the overall sentiment surrounding the merger by processing and analyzing millions of text-based data points, whether from news articles, social media platforms, or public forums. Techniques like sentiment analysis tools powered by Natural Language Processing models like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) or RoBERTa (Robustly Optimized BERT) use deep learning to classify the sentiment of textual content as positive, negative, or neutral. These transformer-based models capture context and nuances in text, making them highly effective for financial sentiment analysis.
In addition to sentiment detection, deep learning enables advanced contextualization of this data by correlating it with other business news triggered by the event or with structured financial data (Ex: historical stock performance or earnings reports) using time series models like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), offering a better understanding of market mood. Furthermore, machine learning tools for topic detection add another layer of analysis by identifying trending themes or recurring discussions, enabling a more nuanced understanding of public discourse surrounding a given event. These insights are synthesized with sentiment scores and financial metrics to predict how stock prices are likely to react, enabling analysts and investors to make more informed decisions. By using deep learning and machine learning methodologies, financial professionals can overcome the limitations of manual analysis. These technologies process real-time data at scale, providing a significant edge in navigating the stock market's unpredictable nature.
3. Evolution of Stock Market Prediction

For decades, the pursuit of understanding and anticipating stock market trends has captured the attention of analysts and investors alike, driven by the potential to unlock better decision-making and financial outcomes. Analysts traditionally rely on two primary approaches: Fundamental analysis and Technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis involves assessing a company's financial health and intrinsic value to project a potential stock price. These metrics include not only the key financial indicators, like cash inflows and outflows, equity and revenues, and debt items, but also the broader economic indicators. For example, if a company's profits are smoothly increasing while maintaining a healthy balance sheet, its stock is often considered a solid investment. This method effectively identifies undervalued stocks or companies with strong long-term growth potential, particularly in stable economic conditions. On the other hand, Technical Analysis focuses on identifying patterns in historical price data and trading volumes by using statistical models to predict future price movements. This approach has proven valuable in understanding short-term trends and momentum. Despite their merits, both methods face significant limitations in today’s rapidly evolving markets.
Fundamental analysis often struggles with the time required to process extensive datasets, causing it to miss immediate opportunities. Meanwhile, technical analysis may not consider sudden market disruptions caused by geopolitical events, economic shifts, or technological advancements; hence, they are unreliable in handling highly volatile and noisy financial data. These limitations become more pronounced given the volume and velocity of modern market data, where external shocks or human emotions can amplify market volatility, driving panic selling or irrational optimism and triggering rapid price movements.
The abundance of data available is both a challenge and an opportunity when predicting stock prices. The stock market generates massive amounts of information daily, from historical price data and trading volumes to corporate financial reports, breaking news, regulatory filings, analyst opinions, and social media sentiment. Each data source offers insights into market behavior. Still, their massive scale and variety can be an issue for traditional methods that struggle to effectively process and integrate such diverse inputs. However, AI thrives in data-rich environments.
AI’s application in stock market prediction has shown remarkable results. A recent study showed that AI-driven hedge funds achieved cumulative returns of 34% over a three-year period, markedly outperforming the global hedge fund industry's 12% gain during the same timeframe. This outperformance is attributed to AI's advanced data processing capabilities, enabling the analysis of diverse information sources—including news articles, social media, and economic indicators—to identify patterns and trends that inform investment strategies. During unforeseen events like the COVID-19 pandemic, AI demonstrated adaptability by processing real-time data to navigate market volatility effectively. This demonstrates that an AI model can analyze price fluctuations over decades, correlate them with global economic indicators, and even factor in real-time social media sentiment as these algorithms learn complex patterns and improve their predictive accuracy. More importantly, once the AI model is trained, it can run inference in real-time, which is a significant advantage in financial markets where decisions often require rapid reactions to new information. Additionally, the model can be continuously retrained to incorporate recent data, ensuring its predictions are relevant to dynamic market conditions.
How does AI Enhance Forecasting Accuracy?

Now that we've explored how AI reshapes stock market prediction let's get into some specifics about the corresponding techniques. Consider a scenario where an analyst aims to predict the future closing prices of a company's stock. By applying statistical time series analysis techniques, such as the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model, the analyst can capture linear trends, seasonal patterns, and short-term dependencies in the stock's past price behavior to forecast and make short-run investment decisions.
However, conventional statistical models struggle to grasp such complex non-linear relationships in financial markets. For instance, Linear models assume that data follows a linear progression. This is rarely the case in the stock market, where trends often reverse suddenly or behave in cyclical, non-linear patterns. These models, therefore, may not consider sudden and sharp market shifts; hence, they are unreliable in handling highly volatile and noisy financial data.
Apart from these, traditional methods may not perform well in long-term dependencies. Time series analysis tends to focus on the most recent data, often ignoring the influence of events that happened weeks, months, or even years ago. However, these past events can resurface and significantly affect current stock prices when similar conditions or market triggers occur. Financial data typically exhibits complex temporal dependencies, where the impact of past events can re-emerge, influencing market behavior long after the event itself has passed. This is where more advanced techniques like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks come into play, particularly for capturing market data's sequential and temporal dependencies. Another key AI technique is sentiment analysis, which adds a further dimension to market dynamics by analyzing news, social media, and financial reports on public sentiment. Together, LSTM and sentiment analysis enhance the ability to make better predictions within the stock market by handling huge amounts of real-time data and mining insights to drive more accurate forecasts.
4. Predicting Stock Prices with LSTM and Sentiment Analysis
LSTM is a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) designed for processing and learning patterns from data sequences, which is ideal for stock price predictions drawing from historical trends. LSTM can learn how different market events affect stock prices over various time horizons and adjust its predictions accordingly. LSTMs have been applied in financial markets to predict stock prices. A study illustrated the use of the LSTM network to predict the stock prices of prominent technology companies like Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon. The research deduces that LSTMs can model sequential data with temporal dependencies, better capturing temporal dynamics and enabling them to deliver more accurate predictions.
How is LSTM Working?
LSTM neural networks are made of memory cells and gates, enabling the model to learn from temporal data. These components help the model to retain important information over long periods while discarding irrelevant data, making them particularly effective in time series predictions. To understand how LSTMs achieve this balance, it’s essential to delve into their architectural components:
Memory Cells: Think of a memory cell in an LSTM as a unique type of journal that selectively remembers essential information over time. It maintains two types of memory.
-
Long-Term Memory: This is like keeping a detailed journal of long-term trends. For example, if you’re tracking a stock, the memory cell remembers important patterns, such as whether the stock price usually rises during the holiday season. This long-term memory helps the model understand and recall these recurring patterns over time.
-
Short-Term Memory: The memory cell keeps track of recent events and changes along with long-term notes. If there’s a sudden drop in stock price due to an external factor, this short-term memory helps the LSTM quickly adapt to new information and respond accordingly.
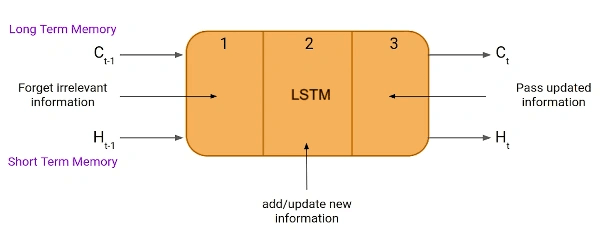 Image Source: Link
Image Source: Link
Gates: The Memory cell doesn’t work alone. It relies on gates to control the flow of information. This means LSTM networks use gates to control what information is kept and what is discarded. There are three types of gates:
- Forget Gate: The forget gate decides what information from the long-term memory should be discarded. It’s like deciding which old trading patterns are no longer relevant.
- Input Gate: The input gate determines what new information should be added to the long-term memory. For example, the input gate adds this to the memory if there’s a new trend in the stock market, like a recent price drop.
- Output Gate: The output gate selects which information from the memory is relevant for making predictions. It combines long-term and short-term memories to produce the final output.

Updating the Memory: Each time new data comes in, the LSTM updates its memory by combining old information with the latest data. For example, if stock prices have been rising smoothly and there’s a new economic report, the LSTM updates its memory to reflect both the long-term trend and the latest information.
LSTM networks excel at analyzing historical stock trends but may struggle to account for sudden market shifts or current investor sentiment. We integrate LSTM with sentiment analysis to enhance predictive accuracy, which evaluates real-time news and public opinions. For example, during the 2019 unveiling of Tesla's Cybertruck, a live demonstration flaw where the vehicle's windows shattered led to a 4.1% drop in Tesla's stock price, highlighting how negative events can swiftly influence investor sentiment and, consequently, stock prices.
What is Sentiment Analysis?

Sentiment Analysis is a technique used to analyze and classify people's opinions, feelings, and attitudes by interpreting written text. It is similar to reading reviews or social media posts to determine whether the public's sentiment is positive, negative, or neutral.
In the stock market, sentiment analysis involves processing large amounts of textual data, including news stories, social media posts, and financial reports, to determine the “pulse” or general mood of investors and the public at scale. For example, suppose reviews and discussions around a tech gadget are positive in the majority. In that case, it might signal a potential increase in the stock price for the company behind the product. Sentiment analysis provides a layer of insight beyond historical price movements by examining how people feel about certain events or companies. Understanding these sentiments allows predictions about their influence on stock prices, offering investors a deeper context for decision-making. Recent advancements in sentiment analysis utilize language models like BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and GPT-4. These models are powerful because they understand context and nuances in text, making them very effective at accurately gauging sentiment from diverse sources.
How Does it Work?
- Data Collection: The process begins by collecting text data from different sources, such as news websites, X (formerly known as Twitter), or financial blogs.
- Processing Text: This collected text undergoes processing through Natural Language Processing techniques to identify and extract relevant information in the text.
- Sentiment Classification: The processed text is then categorized into positive, negative, or neutral classes by algorithms previously trained on large datasets of text examples.
Sentiment Analysis combined with LSTM models leads to a robust and comprehensive approach to predicting stock prices. This combination uses the strengths of both methods, considering historical trends and current sentiments in the market. The image below shows the overall architecture of this Hybrid Approach.
 LSTM x Sentiment Analysis Approach For Stock Price Prediction
LSTM x Sentiment Analysis Approach For Stock Price Prediction
Real-World Applications in Financial Markets
Integrating artificial intelligence into stock market forecasting has become a significant focus of academic research and industry applications. Recent advances in natural language processing and deep learning have led to the development of specialized models that can process historical price data and market sentiment derived from news and social media. Among these innovations, language models specifically trained on financial data have emerged as powerful tools for understanding market dynamics.
FinBERT is a specialized adaptation of BERT's architecture for financial applications. It is fine-tuned on a vast collection of financial documents to adapt its language understanding capabilities specifically to the financial domain. While the original BERT model possesses a broad understanding of general language, fine-tuning recalibrates its neural networks to recognize and interpret finance-specific terminology, jargon, and contextual relationships. This specialized training enables FinBERT to better capture the nuanced sentiments in financial news, reports, and social media, making it adept at understanding the emotional tone of financial text. The FinBERT-LSTM hybrid model combines FINBERT, a trained Natural Language Processing (NLP) model specialized in financial text, with LSTM networks to enhance the accuracy of stock price prediction. This enables historical stock data and news sentiments to be considered in real time to provide an overall predictive approach toward market movements.
a. Predicting NASDAQ-100 Index
A recent study evaluated three deep learning architectures - Fin-BERT Embedding LSTM Architecture, LSTM Architecture, and Classic Deep Neural Network (DNN) Architecture - for predicting NASDAQ-100 Index movements. The FinBERT-LSTM hybrid model, which combines news sentiment analysis with price prediction, demonstrated the strongest performance. However, a well-architected LSTM model trained on extensive historical market data also showed impressive results, achieving only 3% lower accuracy than the hybrid approach. This finding suggests that while sentiment analysis from news can provide additional insights, sophisticated deep-learning models focused purely on price patterns can still capture market dynamics effectively. The key lies in the model's ability to identify complex patterns in historical data, especially when trained on extensive market information spanning different economic cycles.
b. Forecasting the S&P 500 Index
Researchers developed the LSTM-NYT model, which combines stock price data with a "Sentiment Score" derived from analyzing daily news summaries from The New York Times using FinBERT. The study found that the LSTM-NYT model, with its integrated sentiment analysis, significantly outperformed a standard LSTM model that relied solely on historical stock price data. The LSTM-NYT model achieved an R² value (A statistical measure that indicates how well a model fits the data) of 0.8950, compared to 0.8339 for the LSTM-Only model, demonstrating how carefully designed neural architectures that combine multiple data modalities can capture variations in the S&P 500 index.
c. Next-Generation Sentiment Analysis: BloombergGPT
Taking sentiment analysis to the next level, BloombergGPT is a 50-billion-parameter language model developed by Bloomberg and explicitly designed to perform outstandingly within financial contexts. Unlike general-purpose models, BloombergGPT is fine-tuned on a richly diverse set of financial documents, uniquely suited for predicting market movements based on real-time news. BloombergGPT achieved state-of-the-art results on various financial sentiment analysis tasks, outperforming general-purpose LLMs like GPT-3 and GPT-NeoX. The model’s ability to process real-time news and social media data made it particularly effective in predicting market reactions to breaking news.
6. Conclusion
Predicting the stock market trend is very complex and challenging, requiring long-term historical data and an understanding of current market conditions. Traditional analytical frameworks, while foundational, have reached their natural limits in an environment where an unprecedented volume of real-time data and complex global interconnections dictates market movements. In this regard, integrating AI models such as LSTM networks with sentiment analysis is much more than a simple technological enhancement; this introduces a completely new paradigm to the field of market intelligence.
LSTM networks excel at capturing long-term trends and patterns by using their memory cells and gating mechanisms to retain and process relevant historical information at scale. However, relying solely on historical data can cause some inaccuracies in prediction, as it doesn’t account for the ever-changing landscape of market sentiment influenced by current events and public opinion. Sentiment analysis thus comes in handy, defining the real-time market sentiment elicited from news, social media, and other sources. By integrating sentiment analysis with LSTM models, we build resilience in the framework of prediction, one in which both the deep-seated trends and instant reactions of the market are captured, hence making more accurate forecasts.
It is important to remember that this technological advancement comes with important caveats. Advanced models require significant computational resources and may struggle to adapt to unprecedented events, which could limit their effectiveness in certain situations. However, when compared to previous traditional AI approaches, these innovative methods offer a significant leap forward in capturing complex market dynamics and enabling more informed decision-making. With AI integrated into the process, the future of market analysis will not make volatility vanish but will provide more data-driven tools for understanding and navigating uncertainty.






