2026-02-06
Manufacturing has always been about progress. From steam engines to assembly lines, every leap in technology has reshaped how factories work. Today, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the next big leap. It helps businesses make better decisions, reduce delays and improve overall efficiency. Studies suggest that AI could boost manufacturing productivity by up to 40% by 2035, while reducing operational costs by as much as 20%. With global investment in AI for manufacturing expected to reach $8.57 billion by 2025 [1], manufacturers are increasingly using AI to improve planning, monitoring, and operations.
Predictive Maintenance: Fixing Problems Before They Happen
In traditional factories, maintenance was reactive when machines broke down, production stopped, and engineers scrambled to fix the issue. AI changes this by enabling predictive maintenance. Sensors embedded in machines continuously collect data on vibration, temperature, and pressure. Machine learning algorithms then analyze this data to detect anomalies and forecast failures before they occur. For example, an AI system can recognize that a motor’s vibration pattern is deviating from its normal baseline. Instead of waiting for the motor to fail, the system alerts engineers to replace or repair it during scheduled downtime. This reduces unexpected breakdowns, cuts maintenance costs, and extends equipment lifespan. Predictive maintenance often uses time-series analysis and anomaly detection models like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or autoencoders. RNNs are effective because they can analyze sequences of data over time, remembering past inputs to predict future patterns. This makes them ideal for detecting gradual deviations in machine behavior. Siemens’ predictive maintenance platform uses machine learning to analyze real‑time sensor data from industrial equipment, including vibration, temperature, and other operating conditions. One of the early adopters of this system is the Australian steel manufacturer BlueScope Steel. In this setup, machine learning models detect patterns that indicate potential machine issues. By forecasting failures before they happen, engineers can schedule maintenance during planned downtime instead of reacting to unexpected breakdowns. This proactive maintenance approach leads to fewer breakdowns, better resource planning, and measurable cost savings.
 Refer source Here
Refer source Here
Quality Control: Catching Defects Early
Quality control has always been a challenge in manufacturing. Supervisors can miss defects, especially when thousands of products roll off the line every hour. AI-powered computer vision systems now act as tireless inspectors, scanning products in real time and catching even the smallest imperfections. These systems use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on thousands of images of both flawless and defective products. Once deployed, they can identify scratches, misalignments, or irregularities with near-perfect accuracy. For instance, in automotive manufacturing, AI vision systems can detect microscopic paint defects that would otherwise escape human eyes. This ensures that only flawless cars reach customers, reducing recalls and warranty claims. One clear example comes from Samsung’s smartphone factories, where AI-powered vision systems scan screens for tiny scratches or pixel defects that human inspectors might miss. By catching flaws early, Samsung reduces waste and ensures customers receive flawless devices.
Supply Chain Optimization: Making Complexity Simple
Global supply chains are complex webs of suppliers, warehouses, and distributors. AI helps manufacturers manage this complexity by predicting demand, optimizing inventory, and rerouting logistics when disruptions occur. AI models can optimize many aspects of the supply chain, including demand forecasting, inventory allocation, transportation routing, and warehouse operations. A prominent real‑world example is UPS’s ORION (On‑Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system. ORION uses machine learning and advanced analytics to plan and continuously refine delivery routes for the company’s fleet of tens of thousands of vehicles. By evaluating hundreds of thousands of routing options each day based on traffic, delivery windows, and package data, ORION significantly reduces inefficiencies in last‑mile delivery. Since its rollout, UPS has achieved measurable impacts: its optimized routing has cut 100 million miles from delivery routes annually, saved around 10 million gallons of fuel per year, reduced 100,000 metric tons of CO₂ emissions annually, and generated $300–$400 million in annual operational savings through lower fuel and labor costs. These improvements also contribute to better on‑time delivery performance and overall service reliability [2]. By implementing AI‑driven systems like ORION, companies can reduce excess inventory, avoid delays, and respond more flexibly to disruptions. In industries where demand shifts rapidly, such optimization can make the difference between meeting market demand and losing customers.
AI Copilots: Making Knowledge Work for Everyone
AI helps workers do their jobs better, faster, and with more confidence. Many factory managers and engineers don’t have deep technical expertise, but they still need quick access to information. AI copilots make this possible by allowing staff to ask questions in plain language and get precise answers.
Rootcode’s work with Kendrion, a global manufacturing company, is a great example. Kendrion had years of knowledge locked away in PDFs and files. Rootcode built an AI Co-pilot using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which combines natural language processing with document retrieval. Managers can simply ask, “What were the specifications for Project X in 2010?” and instantly get the right document and answer.
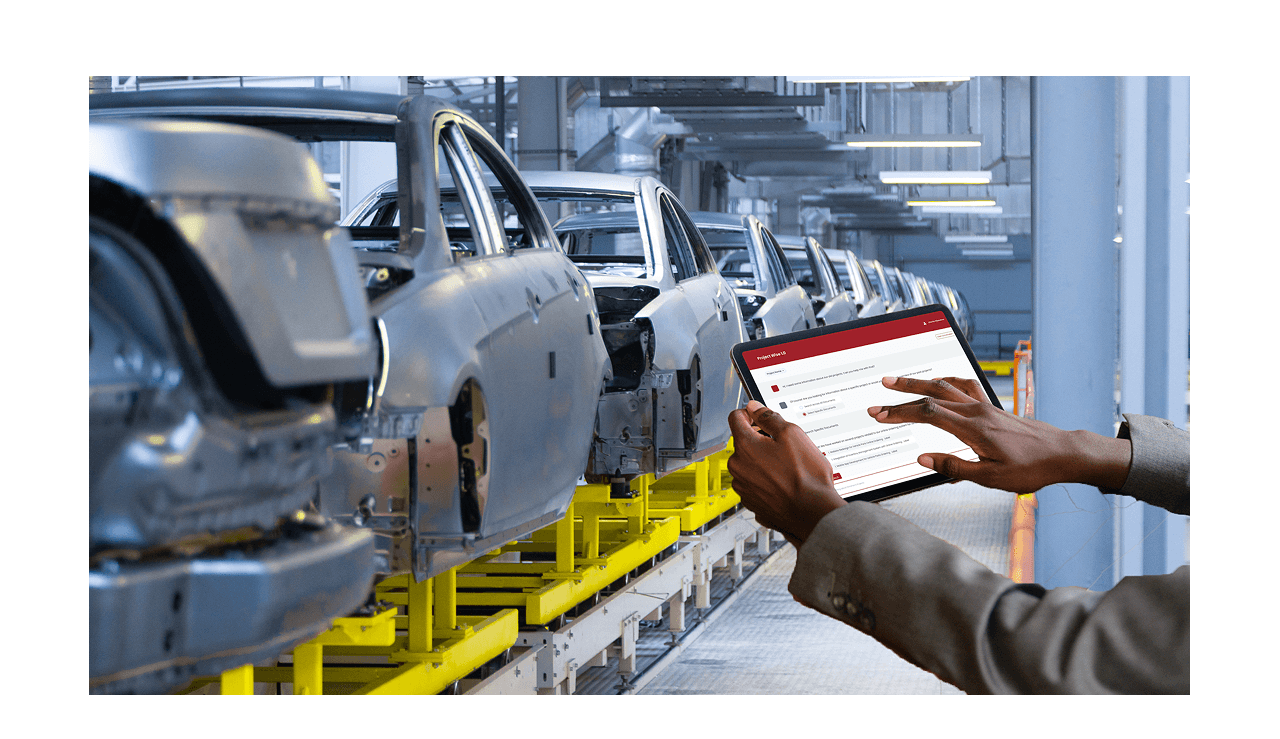
Technically, RAG works by embedding documents into vector space using models like BERT or Sentence Transformers, then retrieving the most relevant passages before generating a natural-language response. This democratizes access to knowledge, making decision-making faster and smarter without requiring technical skills.
Robotics: Smarter Automation on the Floor
Robots have been part of manufacturing for decades, but AI makes them adaptive. Instead of following rigid instructions, AI-powered robots can learn, adjust, and even collaborate with humans.
Modern robots use reinforcement learning to improve their performance over time. For example, a welding robot can adjust its technique based on sensor feedback, ensuring precision even when materials vary slightly. Collaborative robots (“cobots”) are designed to work safely alongside humans, using AI to detect human presence and adapt their movements accordingly.
This flexibility means factories can respond quickly to new product designs or sudden changes in demand. AI-driven robotics turn traditional assembly lines into living systems that evolve with the business.
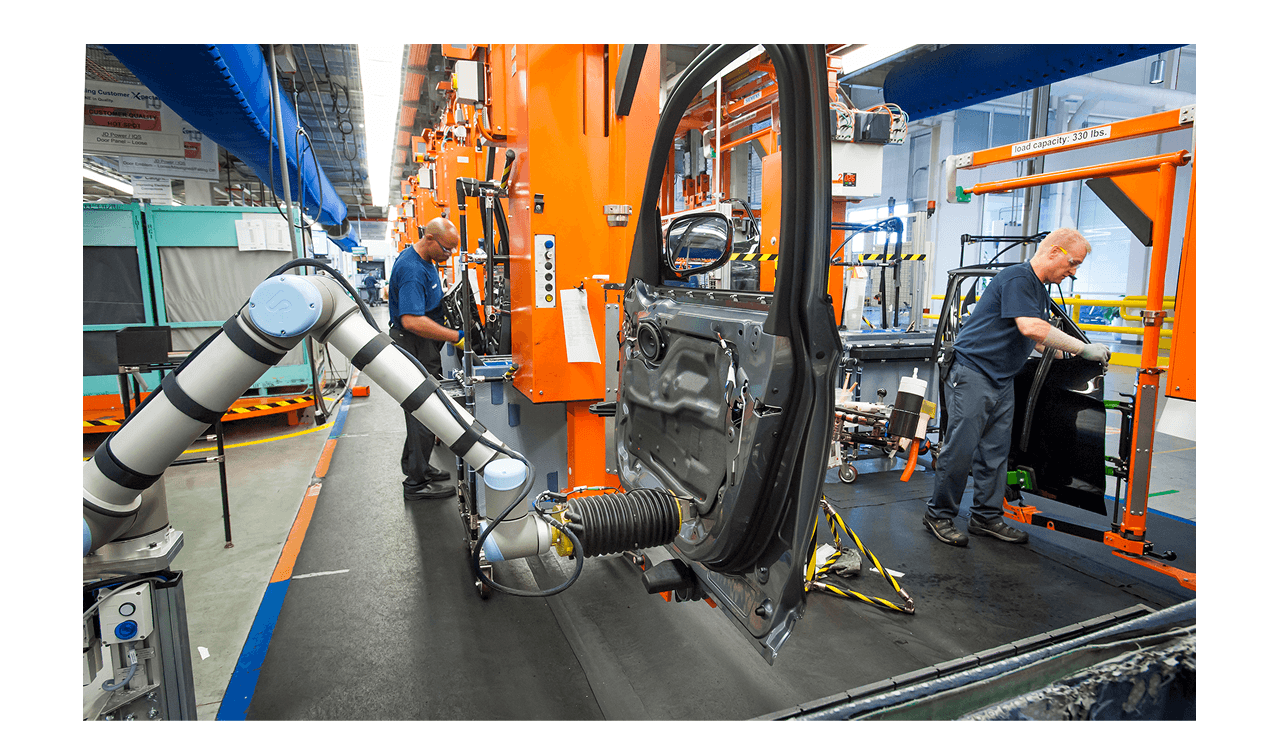
BMW shows how this works in practice. The company uses AI-powered collaborative robots on its production lines to assist workers with tasks like lifting heavy parts and welding. These robots adjust their movements in real time when humans are nearby, making the workspace safer and more efficient.
 Refer source Here
Refer source Here
Challenges Along the Way
Adopting AI in manufacturing is not straightforward. Many factories still depend on legacy infrastructure, with machines and IT systems that struggle to integrate with modern AI platforms. Upgrading these systems requires significant investment, and the fear of disrupting ongoing operations often slows progress. Another hurdle is the shortage of skilled talent. AI engineers and data scientists are in high demand across industries, and manufacturing companies often find it difficult to compete with tech firms for expertise. This lack of talent means many projects stall at the pilot stage, unable to scale across entire operations. At the same time, organizations face the “productivity paradox,” where short-term dips occur before long-term gains, as employees adapt to new workflows and processes. To resolve this skills gap, Rootcode offers an Extended Teams service that lets you scale your tech workforce up or down instantly. Our experts plug directly into your operations and work as a seamless part of your own team, giving you the specialized talent you need without the long hiring delays. Finally, manufacturers must address ethical, regulatory, and cultural challenges. AI decisions need to be explainable, especially when product safety is at stake. Data privacy and cybersecurity are critical as factories become more connected, and workers must be reassured that AI is designed to support rather than replace them. Building trust in both the technology and its role in the workplace is essential for successful adoption.
Conclusion
AI is becoming a core part of how modern manufacturing operates. It predicts problems before they happen, ensures consistent quality, balances supply chains, empowers workers, and makes robots smarter. By embracing AI, manufacturers can reduce costs, increase productivity, and deliver better products, all while creating workplaces where humans and machines collaborate effectively. Rootcode delivers secure, domain-specific AI solutions for manufacturing. We help governments and enterprises move from pilots to full-scale adoption by building systems that integrate with existing infrastructure, strengthen data security, and provide clear, explainable results. Our solutions cover areas such as predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and AI-powered quality control, ensuring manufacturers achieve measurable improvements in efficiency and reliability. Ready to transform your business with AI? Let’s talk.






